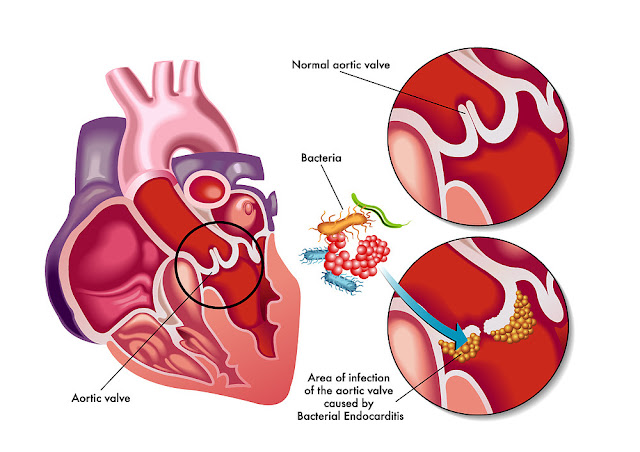
MITRAL STENOSIS
Definition
- Mitral valve thickens and gets narrower, blocking blood flow fro. the left atrium to left ventricle
Physiology
- Function of the heart is the transport of oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients and waste products
- Cardiac cycle consists of:
- Systole - the phase of contraction during which the chambers eject blood
- Diastole - the phase of relaxation during which the chambers fill with blood. When heart pumps, myocardial layer contracts and relaxes.
- Blood flow:
- Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium through the superior and inferior vena cava
- Enters the right ventricle via the tricuspid valve
- Travels through the pulmonic valve to pulmonary arteries and lungs
- Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium and enters the left ventricle via the bicuspid (mitral) valve
- From the left ventricle, through the aortic valve through the aorta to the systemic cicrculation
- The heart itself is supplied with blood by the left and right coronary arteries
- The vascular system is a continuous network of blood vessels
- the arterial system consists of arteries, arterioles and capillaries and delivers oxygenated blood to tissues
- Oxygen, nutrients and metabolic waste are exchanged at the cellular level
- The venous system, veins and venules, returns the blood to the heart