- art of getting things done through people
- process of getting activities completed efficiently and effectively with and through people in order to attain goals of the organization
Principles of Management
- Division of Labor - specialization leads to efficient work performance
- Authority - managers give orders to make things done
- Discipline - members of organization respect rules and agreements that govern organization
- Unity of Command - a member receives instruction from only one superior
- Unity of Direction - common objective(s) for the entire organization
- Subordination of the common interest for the common good - organizational interests take precedence over personal interests
- Renumeration - fair compensation is based on work done
- Centralization/Decentralization - the role of subordinates in decision-making may be decreasing (centralization) or increasing (decentralization)
- Hierarchy - the line of authority of the organization is the order of rank from the top managers to the lowest segment of the enterprise
- Order - materials and people are at the right time at the right place
- Equity - managers exercise fairness to subordinates
- Stability of Staff - a low employee turn-over rate brings about an efficient functioning of the organization
- Initiative - members have the freedom to conceive and carry out their plans
- Esprit de Corps - team spirit gives a sense of unity
Theories of Management
- Approaches -> Emphasis
- Classical - worker efficiency "one right way" to perform a task
- Behavioral - Understanding the worker to improve efficiency
- Management Science - Scientific method to improve productivity and organizational effectiveness
- Contingency - The best approach to problem vary depending on situations
Classical Theories
- Frederick Taylor
- scientific management theory
- "the productivity will increase through careful, systematic design of workplace conditions, work methods and proper training and instruction of workers"
- Fundamental Principles:
- The development of a true science of management to determine the best method for task performance
- The scientific selection of worker towards provision of responsibility for the task which he/she is best suited
- The scientific education and development of worker
- The intimate, friendly cooperation between management and workers
- Frank and Lilian Gilbreth - motion studies
- Henri Fayol
- administrative theory
- "with scientific forecasting and proper methods of management, satisfactory results were inevitable"
- Henry Gantt
- scheduling and rewarding employees
- developed the Gantt Chart which is a tool for displaying the progression of a project in a form of specialized chart
- provides a graphical illustration of a schedule that helps to plan, coordinate and track specific tasks in a project
- Max Weber
- bureaucracy for complex organizations
- organizations with hierarchical structure are most efficient and effective
- Characteristics of Bureaucratic Organization:
- tasks are specialized
- person is appointed by merit because of ability and not of favoritism or whim
- career opportunities are provided
- authority and responsibility are specified
- activities are routinized
- a rational and impersonal climate exists
Behavioral Theories
- Elton Mayo
- Hawthorne experiments
- founder of human relations movement
- Hawthorne effect describes a temporary change to behavior or performance in response to a change in the environmental conditions, with the response being typically an improvement
- Mary Parker Follett
- conflict resolution human approach to organizational design
- Chester Barnard
- acceptance theory of authority
- Douglas McGregor
- Theory X and Theory Y:
- Theory X
- Average person is inherently lazy; does not like work and will try to avoid it; works to survive
- Avoids responsibility; prefers to be directed rather than act independently; little or no ambition, not too intelligent; wants only security
- Manager must exercise strict control to ensure work is carried out properly
- Theory Y
- Views human nature positively
- People regard work as a source of satisfaction; accept and seek responsibility
- Work is motivating and rewarding
- Manager provides opportunities for the subordinates to be creative and productive and to encourage growth and guidance
- Rensis Likert
- participative management
- Robert Blake and Jane Mouton
- Management grid
- leaders may be concerned for their people and they also must have some concern for the work to be done
Impoverished Management
- minimum effort to get the work done
- basically a lazy approach that avoid as much work as possible
- strong focus on task, but with little concern for people
- focus on efficiency, including the elimination of people wherever possible
- care and concern for the people, with a comfortable and friendly environment and collegial style
- but a low focus on task may give questionable results
Middle of the Road Management
- A weak balance of focus on both people and the work
- Doing enough to get things done but not pushing the boundaries of what may be possible
Team Management
- Firing on all cylinders: people are committed to task and leader is committed to people (as well as task)
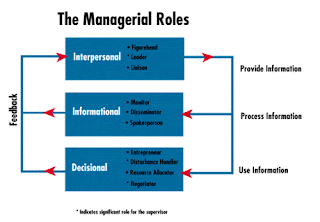
- Henry Mintzberg
- 10 Roles of a Manager
- FIGUREHEAD - the manager performs ceremonial and symbolic duties as head of the organization
- LEADER - fosters a proper work atmosphere and motivates and develops subordinates
- LIAISON - develops and maintains a network of external contacts to gather information
- MONITOR - gathers internal and external information relevant to the organization
- DISSEMINATOR - transmits factual and value based information to subordinates
- SPOKESPERSON - communicates to the outside world on performance and policies
- ENTERPRENEUR - designs and initiates change in the organization
- DISTURBANCE HANDLER - deals with unexpected events and operational breakdowns
- RESOURCE ALLOCATOR - controls and authorizes the use of organizational resources
- NEGOTIATOR - participated in negotiation activities with other organizations and individual
- Fritz Roethlisberger
- psychological factors affect work output
- no simple correlation between physical working conditions and work output
- factors such as: support from fellow workers, participative decision-making and recognition from administrators all influence productivity
- Kurt Lewin
- field theory of human behavior
- worker's behavior is influenced by interactions between worker's personality, structure of primary work group and socioethical climate of workplace
- process of attitudes and behavior change occurs in three phases:
- Unfreezing - equilibrium is upset
- Changing - new attitudes and behavior
- Refreezing - integration of new attitudes, behavior into worker's personality and relationships
- William Ouchi
- Theory Z
- Workers are the keys to increase productivity
- Characteristics
- Long term employment
- Slower production
- Collective decision making
- Indirect supervision
Fiedler and Cherners
- postulates that there is no best way for managers to lead
- situations will create different leadership style requirements for a manager
- the solution to a managerial situation is contingent on the factors that impinge on the situation
- Fiedler looked at three situations that could define the condition of a managerial task:
- Leader-Member Relations - are the amount of loyalty, dependability ad support that the leader receives from employees
- Task Structure - in a favorable relationship the manager has a high task problems; in an unfavorable relationship the task is usually unstructured and the leader possesses limited authority
- Position Power - measures the amount of power or authority the manager perceives the organization has given him or her for the purpose of directing, rewarding and punishing subordinates
- The Path-Goal theory developed by Robert House is based on the expectancy theory of motivation
- The manager's job is viewed as coaching or guiding workers to choose the best paths for reaching their goals
- "Best" is judged by the accompanying achievement of organizational goals
- It is based on the precepts of goal setting theory and argues that leaders will have to engage in different types of leadership behavior depending on the nature and demands of the particular situation
- Top Managers - responsible for the overall operations of nursing services; establish objectives, policies and strategies; represent the organization in community affairs, business arrangements and negotiations; typical titles: director of nursing services, chairman, executive vice president
- Middle Managers - usually coordinate the nursing activities of several units, receive broad, overall strategies and policies from top managers and translate them into specific objectives and programs; typical titles: supervisor, coordinator
- First-Line Managers - directly responsible for the actual production of nursing services; act as links between higher level managers and nonmanagers; typical titles: head nurse, team leader, primary care nurse


Nice. Read also on Human Relations Theory of Management.
ReplyDelete